Improve your biologics and antibody development with 2bind’s expertise in multi-parameter HPLC Analytics.
Meet the one-for-all tool for protein and antibody analytics: The Agilent Infinity HPLC system with SEC, HIC, and IEX colums, coupled to Wyatt MALS and RI detectors. This setup provides all the important developability parameters of your antibody or biologic: Molecular weight, oligomerization state, hydrophobicity, charge-state and charge-variants.
Our customized assays, paired with expert data interpretation, ensure high-quality data and actionable results. Choose 2bind for faster turnaround times, superior sensitivity, and unparalleled support at every step.
High performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) separates the contents of liquid or solid samples on chromatography columns. The type of column and the running buffer define the parameters of separation, the application of the system, and the questions that can be answered with it.
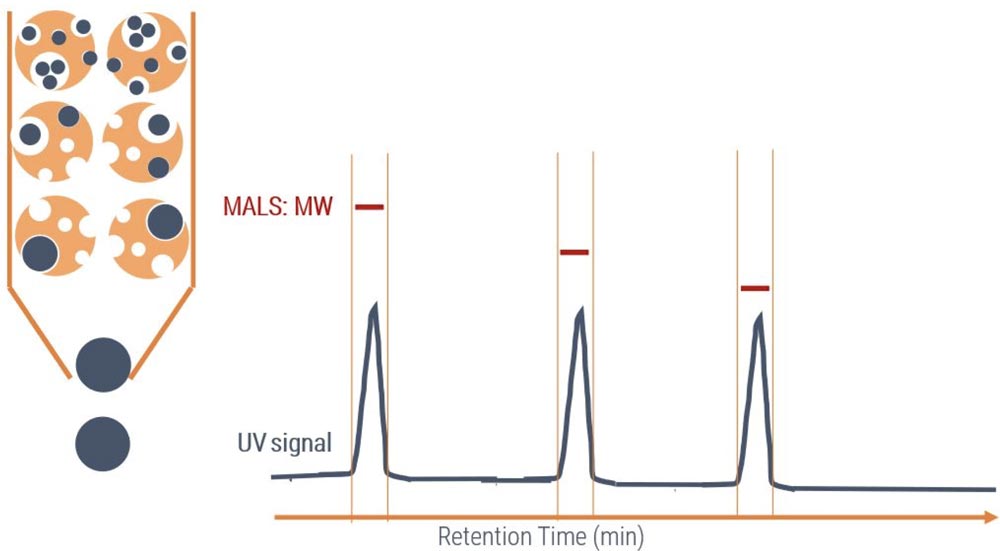
SEC (Size-Exclusion Chromatography) separates protein or antibody samples by their molecular weight or oligomeric state. When coupled to a MALS (Multi-Angle Light-Scattering) detector, the precise molecular weight of samples can be determined. Molecular weight, oligomeric state, and purity are important developability markers of antibodies.
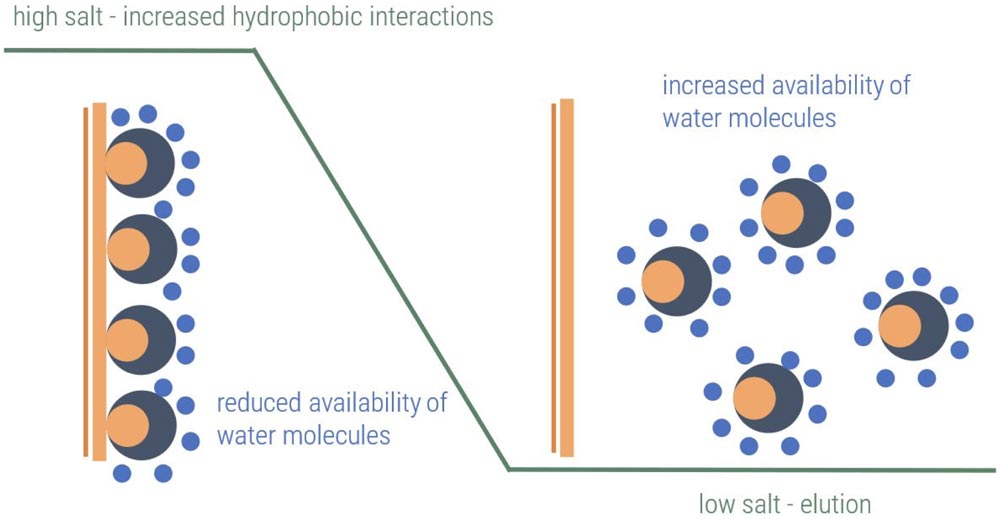
HIC (Hydrophobic Interaction Chromatography) separates protein or antibody samples by their overall hydrophobicity, i.e. their tendency to interact with hydrophobic phases. Important developability marker for antibodies.
IEX (Ion-Exchange Chromatography) separates protein or antibody samples by their surface charge profile. Differences in these surface charges can arise from post-translational modifications or from different charge variants. They are also important developability markers of antibodies.
High-precision and calibration-free measurement of protein molecular weight via light scattering.
Protein fragments, oligomers, and aggregates are visible in SEC-MALS profiles.
Accurate molecular weight determination from SEC-MALS gives composition of protein complexes.
Size-dependent separation of proteins shows impurities and byproducts of a sample.
Longer retention time means higher hydrophobicity. Important developability marker for antibodies.
Hydrophobicity-based, size-independent separation of proteins shows impurities and byproducts.
High-precision and calibration-free measurement of protein molecular weight via light scattering.
Retention time depends on protein surface charge. Important developability marker for antibodies.
PTMs can influence the surface charge distribution of proteins; identified and differentiated from ion-exchange profiles.
Charge-based, size-independent separation of proteins shows impurities and byproducts.
High-precision and calibration-free measurement of protein molecular weight via light scattering.
A clean SEC profile is typically included in every batch-release data package because it reveals size-dependent heterogeneity in the sample. SEC profiles are considered during antibody engineering and lead candidate selection, and candidates with the cleanest profiles are chosen for subsequent drug development.
The hydrophobicity of different antibody candidates is typically compared using HIC. Increased hydrophobicity is a well-known risk factor for developability issues, which can result in off-target reactivity and poor pharmacokinetics (PK). Hydrophobicity is thus considered during lead candidate selection as a strategy to reduce the risk of failure due to developability issues.
The drug-to-antibody ratio (DAR) and the site of drug-conjugation are important parameters for ADC characterization. HIC can separate molecules that differ in DAR or in the position of the drug.
The glycan mass per glycoprotein can be determined in the triple detection system, using MALS-UV-RI. For example, different glycan mass of the same glycoprotein produced in insect and mammalian cells can be detected.

Whereas FPLC is the method of choice for preparative separations of proteins, HPLC provides better resolution and higher quality analytical data.
Only 50 µg of protein are required for one HPLC run.
Sensitivity for impurities depends on the amount of loaded sample. Non-UV absorbing contaminations can be detected in the refractive index (RI) profile.
With the current system we can separate proteins in a range of 10 to 600 kDa. Factor 2 differences in molecular weight typically result in separated peaks, smaller differences will appear as shoulder or tailing in the chromatogram.
We use established positive and negative controls and use the retention time on the HIC column to rank the antibodies in relation to the controls.